Quick and simple breakdown of the 3D printing process.
Introduction to 3D Printing
3D printing is an additive manufacturing process originally developed to enable companies to rapidly prototype as opposed to traditional methods such as clay, wood or other variations of fabrication.
3D Printing Technology

The two most common 3D printing technologies are Filament and Resin 3D printing.
Filament 3D printing technology is known as Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF).
The most common Resin 3D printing technology is Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) and Digital Light Processing (DLP).
What is Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF) 3D Printing?

Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF) is the most common form of 3D printing available in the market today. FFF printing is a process where plastic printing filament is extruded through a heated nozzle and the first layer is deposited onto the build platform. Due to the heat each subsequent layer becomes fused with the layer underneath.
This process is repeated until all layers that form the 3D model are completed.
What are plastic printing filament?

Plastic printing filament commonly comes in 1.75mm width and spool sizes can range between 500g-1kg. The most common plastics for 3D printing are listed below;
- PLA, Polylactic Acid
- ABS, Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene
- PETG, Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol
- TPE/TPU/TPC, Thermoplastic Elastomers
- Nylon
3D Print For Me primarily uses PLA, we prefer this material as it is one of the most environmentally friendly filaments in the market, PLA is derived from crops such as corn and sugarcane which most importantly is biodegradable under certain conditions.
What is Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) 3D Printing?
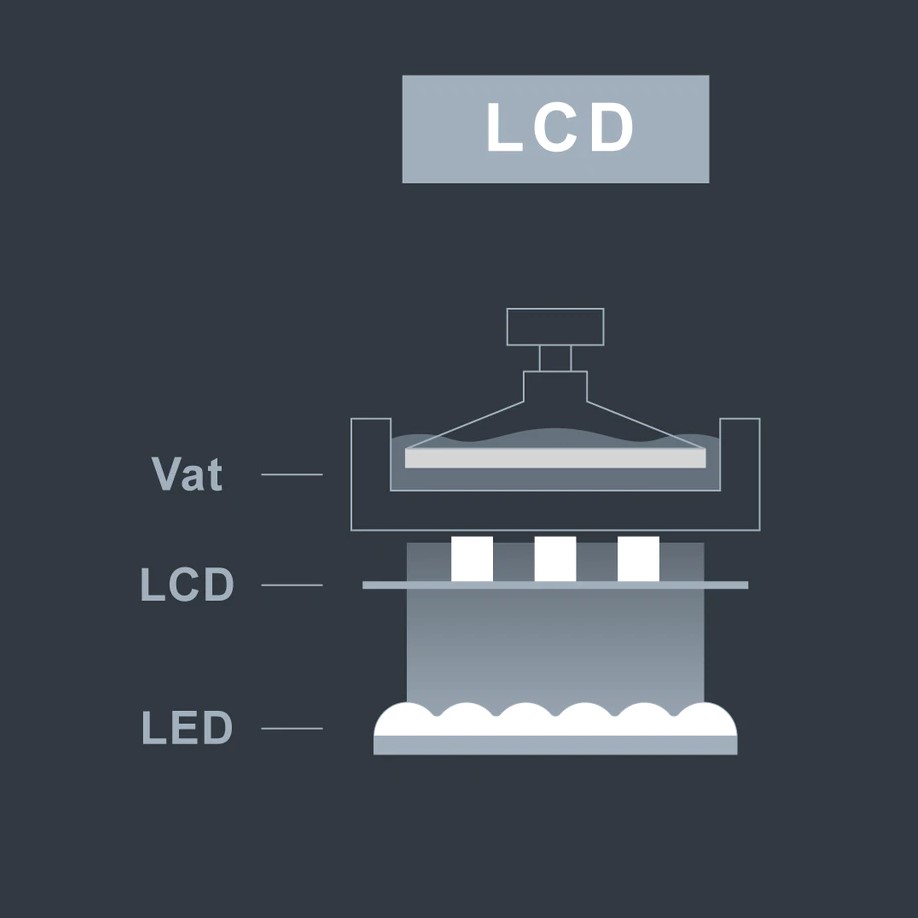
LCD 3D printers use a combination of Ultraviolet LED light and a LCD Colour /Mono display screens, these screens are similar to a display screen found on regular tablets. The LCD controls the light pattern by displaying a specific pattern to allow LED light to pass through and cure the resin in the resin vat. The LCD holds this pattern for approximately 6-8 seconds per layer to allow sufficient time for the resin to cure before displaying the pattern for the next layer.
Once a layer is cured the build platform lifts up just enough to peel off the layer of cured resin from the bottom of the resin vat and allow uncured resin to fill the void before the next layer pattern is displayed by the LCD.
This process is repeated until all layers that form the 3D model are completed.
What is Digital Light Processing (DLP) 3D Printing?
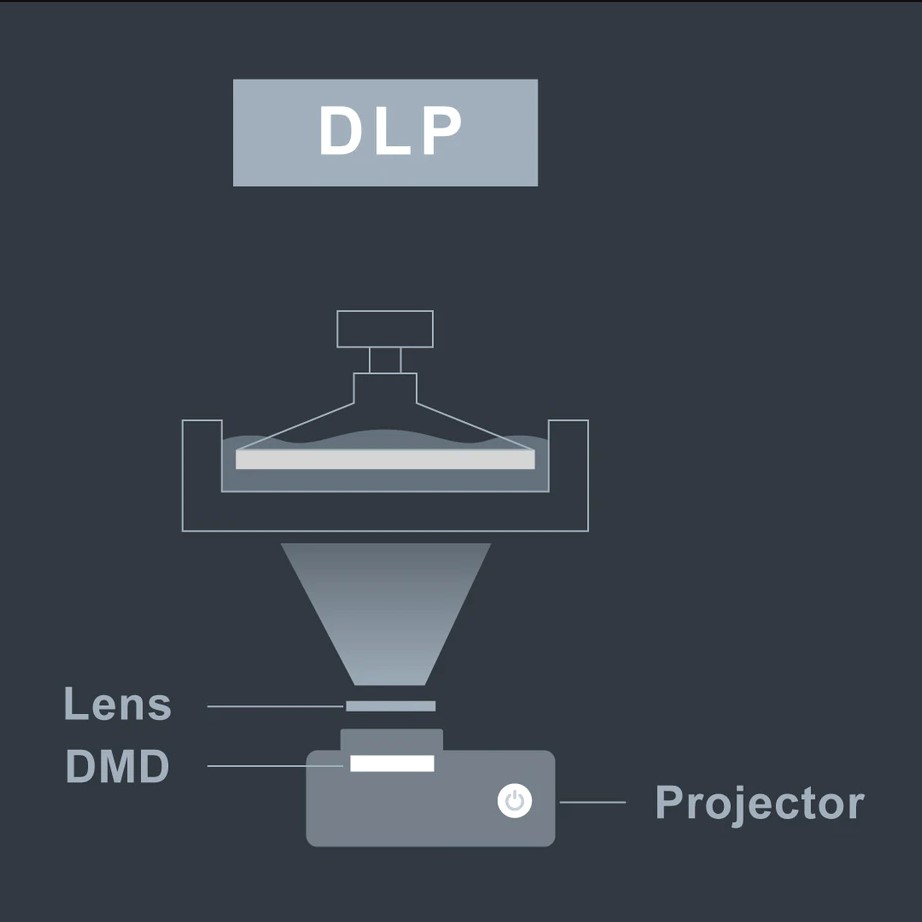
Digital Light Processing (DLP) is much similar to the LCD 3D Printing however the LCD and LED Light are replaced by a Projector and Lens.
The projector flashes Ultraviolet (UV) light in a similar fashion to cure resin in the resin vat. The light pattern displayed is generated by a Digital Micromirror Device (DMD) inside the projector lens.
Once a layer is cured the build platform lifts up just enough to peel off the layer of cured resin from the bottom of the resin vat and allow uncured resin to fill the void before the next layer pattern is displayed by the projector.
This process is repeated until all layers that form the 3D model are completed.
